Identification
Moles are cylindrical, torpedo shaped. They are often mistaken as mice or rats when seen. The most notable aspect of the mole is its large, powerful front feet, designed for pushing soil out of its way. The eastern mole has an average total length of 5.5 to 6 inches and a short, sparsely haired tail 1 to 1.5 inches long. Their eyes are small, concealed beneath the fur, and used only for detecting light and darkness. Moles have no external ears with their ear canals concealed within the fur. They also have no visible neck.
Life History
The eastern mole prefers loose, well- drained soils. The mole’s nest chamber is 4 to 6 inches in diameter and lined with fine grass and leaves. Moles have one litter of 2 to 5 young per year. The young are born in early spring after a 45 day gestation period. Moles live for about 3 years.The characteristic mole ridges that lie just below the surface are foraging tunnels. These tunnels are created as the mole searches among the plant roots for earthworms and insects.
Diet
Moles eat mole crickets, Beetle larvae (White grubs, Japanese beetle grubs), ants and slugs.
Tunnels
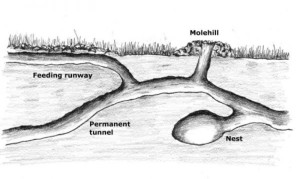
Surface tunnels are most commonly noticed because of the raised ridges running through lawn areas. In loose soil, moles can tunnel up to 18 ft. in a 24 hour period. Surface runs may be used daily, or used only once and then abandoned. They connect with deep runways, which are located between 3 and 12 inches below the surface. The nest is located in one of the deep runways.
or used only once and then abandoned. They connect with deep runways, which are located between 3 and 12 inches below the surface. The nest is located in one of the deep runways.
Mole Damage
The damage caused by moles is cosmetic. Although moles are often falsely accused of eating the roots of grass and other plants, they actually feed on the insects causing the damage. The tunneling of moles causes physical damage to the root systems of sod by drying out the roots
Control Techniques
Habitat Modification
Moles can be discouraged from digging in the turf by controlling the populations of insects on which they feed. This may sound like a correct measure, but may not solve the problem before much damage is done. Be aware that insecticide treatment of an area may cause moles to tunnel more to seek out a diminishing food supply and beneficial insects may also be eliminated. If an insecticide is used, Sevin 80WSP. This may be applied at the rate 3.67 oz. / 1,000 sq. ft.
Fumigants and Baits.
Fumigants have proved of little use in killing moles.Fumigants are not capable of sufficiently penetrating throughout the mole extensive runway system. However, a bait called Talpirid has proven somewhat useful. It is a white digestible material impregnated with a toxin which resembles an earthworm. When using talpirid bait, the homeowner should locate the shallow tunnels that the moles are using. This is done by pressing down with the foot half way down, but not closing the tunnel. Place a flag beside this spot. Do this in several tunnel locations. The next morning, note the tunnels which show a pushing up of sod, and insert 1 talpirid bait at each spot.
Trapping
The most used mole trap is the harpoon trap. The harpoon trap impales the mole with steel spikes when the animal pushes up on the trigger. To locate an active tunnel, press down partially with your shoe, closing the various tunnels 50 percent closed. Re-check the site after 24 hours, and position the harpoon trap above a tunnel that has been pushed back up.Trapping is the easiest and most effective during the spring and fall, when mole surface activity is at a peak.
Conclusion
The damage that moles do is the result of foraging for worms, insects and insect grubs. The 2 ways to reduce their population is (1) baiting them with Talpirid and (2) trapping. There are several home remedies that do not work. They include broken glass, razor blades, rose branches, bleach, moth balls, lye, human hair, car’s exhaust, ultrasonic sounds and Wrigley’s Juicy Fruit Gum. None of these work.